测试环境
openEuler 22.03 (LTS-SP4) 8核20G 120G1、安装helm
# 下载并运行官方安装脚本(需提前安装tar)
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
sudo ./get_helm.sh
# 验证安装
helm version
# 输出: version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.12.3", ...}# 添加国内镜像仓库(如阿里云)
helm repo add aliyun https://kubernetes.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/charts
# 添加dify仓库
helm repo add dify https://langgenius.github.io/dify-helm
# 更新仓库
helm repo update2、k3s部署
curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -
# 1. 创建 ~/.kube 目录
mkdir -p ~/.kube
# 2. 复制 k3s 配置
sudo cp /etc/rancher/k3s/k3s.yaml ~/.kube/config
# 3. 给当前用户可读权限
sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) ~/.kube/config
chmod 600 ~/.kube/config
kubectl get node
# 应该能看到 Ready 的节点
helm version
# 能打印客户端/服务端版本,说明已连通
#测试时openeluer不自带container-selinux >= 3:2.191.0-1的软件源,可自行安装解决
#也可使用跳过:curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io |INSTALL_K3S_SKIP_SELINUX_RPM=true sh -StorageClass
• k3s 默认无 StorageClass
kubectl apply -f local-path-storage.yaml
• 设为默认:
kubectl patch sc local-path -p '{"metadata":{"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
3、下载dify的配置文件
4、代理配置(可选)、这里使用clash
wget http://cloud.supome.cn/clash-amd64-linux%E5%92%8Ccountry.zip
mkdir -p /etc/clash-meta
unzip clash-amd64-linux和country.zip
gzip -d mihomo-linux-amd64-compatible-v1.18.8.gz
mv mihomo-linux-amd64-compatible-v1.18.8 /usr/local/bin/clash-meta
mv Country.nmdb /etc/clash-meta
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/clash-meta
wget -O /etc/clash-meta/config.yaml "https://<你的订阅链接>"vi /etc/systemd/system/clash-meta.service
[Unit]
Description=Clash.Meta Service
After=network.target
[Service]
User=root
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/clash-meta -d /etc/clash-meta
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
#注意selinuxexport http_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:7890
export https_proxy=http://127.0.0.1:78905、安装各个 Charts
kubectl create namespace minio
kubectl create namespace postgresql
kubectl create namespace qdrant
kubectl create namespace redis
kubectl create namespace weaviate安装 MinIO
helm install minio ./minio \
--namespace minio \
--set replicas=1 \
--set persistence.enabled=true \
--set persistence.size=5Gi \
--set mode=standalone
helm install minio ./minio --namespace minio 会占用16*500G
或者使用自定义 values 文件:
helm install minio ./minio -f minio/values.yaml --namespace minio#查看ak、sk
export MINIO_ACCESS_KEY=$(kubectl get secret --namespace minio minio -o jsonpath="{.data.rootUser}" | base64 --decode)
export MINIO_SECRET_KEY=$(kubectl get secret --namespace minio minio -o jsonpath="{.data.rootPassword}" | base64 --decode)
echo "AccessKey: $MINIO_ACCESS_KEY"
echo "SecretKey: $MINIO_SECRET_KEY"
#端口转发,测试用
kubectl port-forward svc/minio 9000:9000 --namespace minio
#创建桶
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$(kubectl get secret -n minio minio -o jsonpath="{.data.rootUser}" | base64 -d) AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$(kubectl get secret -n minio minio -o jsonpath="{.data.rootPassword}" | base64 -d) aws --endpoint-url http://minio.minio.svc.cluster.local:9000 s3 mb s3://dify-storage
#查看桶
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=$(kubectl get secret -n minio minio -o jsonpath="{.data.rootUser}" | base64 -d) AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=$(kubectl get secret -n minio minio -o jsonpath="{.data.rootPassword}" | base64 -d) aws --endpoint-url http://minio.minio.svc.cluster.local:9000 s3 ls helm install minio ./minio --namespace minio --set replicas=1 --set persistence.enabled=true --set persistence.size=5Gi --set mode=standalone
NAME: minio
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Aug 1 13:01:42 2025
NAMESPACE: minio
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
MinIO can be accessed via port 9000 on the following DNS name from within your cluster:
minio.minio.cluster.local
To access MinIO from localhost, run the below commands:
1. export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace minio -l "release=minio" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
2. kubectl port-forward $POD_NAME 9000 --namespace minio
Read more about port forwarding here: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/kubectl/kubectl_port-forward/
You can now access MinIO server on http://localhost:9000. Follow the below steps to connect to MinIO server with mc client:
1. Download the MinIO mc client - https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart
2. export MC_HOST_minio-local=http://$(kubectl get secret --namespace minio minio -o jsonpath="{.data.rootUser}" | base64 --decode):$(kubectl get secret --namespace minio minio -o jsonpath="{.data.rootPassword}" | base64 --decode)@localhost:9000
3. mc ls minio-local
[root@localhost charts]#
安装 PostgreSQL
helm install postgresql ./postgresql --namespace postgresql
#ssl
helm install postgresql ./postgresql \
--namespace postgresql \
--set tls.enabled=true \
--set tls.autoGenerated=true#获取密码
export POSTGRES_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace postgresql postgresql -o jsonpath="{.data.postgres-password}" | base64 -d)
echo $POSTGRES_PASSWORD
#连接
kubectl run postgresql-client --rm --tty -i --restart='Never' --namespace postgresql --image docker.io/bitnami/postgresql:15.3.0-debian-11-r7 --env="PGPASSWORD=$POSTGRES_PASSWORD" \
--command -- psql --host postgresql -U postgres -d postgres -p 5432
#创建数据库
CREATE DATABASE dify;
CREATE DATABASE dify_plugin_daemon;
CREATE DATABASE enterprise;
CREATE DATABASE audit;
\q[root@localhost charts]# helm install postgresql ./postgresql --namespace postgresql
NAME: postgresql
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Aug 1 11:23:28 2025
NAMESPACE: postgresql
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
CHART NAME: postgresql
CHART VERSION: 12.5.6
APP VERSION: 15.3.0
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
PostgreSQL can be accessed via port 5432 on the following DNS names from within your cluster:
postgresql.postgresql.svc.cluster.local - Read/Write connection
To get the password for "postgres" run:
export POSTGRES_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace postgresql postgresql -o jsonpath="{.data.postgres-password}" | base64 -d)
To connect to your database run the following command:
kubectl run postgresql-client --rm --tty -i --restart='Never' --namespace postgresql --image docker.io/bitnami/postgresql:15.3.0-debian-11-r7 --env="PGPASSWORD=$POSTGRES_PASSWORD" \
--command -- psql --host postgresql -U postgres -d postgres -p 5432
> NOTE: If you access the container using bash, make sure that you execute "/opt/bitnami/scripts/postgresql/entrypoint.sh /bin/bash" in order to avoid the error "psql: local user with ID 1001} does not exist"
To connect to your database from outside the cluster execute the following commands:
kubectl port-forward --namespace postgresql svc/postgresql 5432:5432 &
PGPASSWORD="$POSTGRES_PASSWORD" psql --host 127.0.0.1 -U postgres -d postgres -p 5432
WARNING: The configured password will be ignored on new installation in case when previous Posgresql release was deleted through the helm command. In that case, old PVC will have an old password, and setting it through helm won't take effect. Deleting persistent volumes (PVs) will solve the issue.
安装 Qdrant
helm install qdrant ./qdrant --namespace qdrant --set apiKey="test-dify-apikey-qdrant"[root@localhost charts]# helm install qdrant ./qdrant --namespace qdrant --set apiKey="test-dify-apikey-qdrant"
NAME: qdrant
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Aug 1 12:14:37 2025
NAMESPACE: qdrant
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
NOTES:
Qdrant v1.9.0 has been deployed successfully.
The full Qdrant documentation is available at https://qdrant.tech/documentation/.
To forward Qdrant's ports execute one of the following commands:
export POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods --namespace qdrant -l "app.kubernetes.io/name=qdrant,app.kubernetes.io/instance=qdrant" -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
If you want to use Qdrant via http execute the following commands
kubectl --namespace qdrant port-forward $POD_NAME 6333:6333
If you want to use Qdrant via grpc execute the following commands
kubectl --namespace qdrant port-forward $POD_NAME 6334:6334
If you want to use Qdrant via p2p execute the following commands
kubectl --namespace qdrant port-forward $POD_NAME 6335:6335
安装 Redis
helm install redis ./redis --namespace redis#获取密码
export REDIS_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace redis redis -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d)
echo $REDIS_PASSWORD[root@localhost charts]# helm install redis ./redis --namespace redis
NAME: redis
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Aug 1 11:23:50 2025
NAMESPACE: redis
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
NOTES:
CHART NAME: redis
CHART VERSION: 16.13.2
APP VERSION: 6.2.7
** Please be patient while the chart is being deployed **
Redis® can be accessed on the following DNS names from within your cluster:
redis-master.redis.svc.cluster.local for read/write operations (port 6379)
redis-replicas.redis.svc.cluster.local for read-only operations (port 6379)
To get your password run:
export REDIS_PASSWORD=$(kubectl get secret --namespace redis redis -o jsonpath="{.data.redis-password}" | base64 -d)
To connect to your Redis® server:
1. Run a Redis® pod that you can use as a client:
kubectl run --namespace redis redis-client --restart='Never' --env REDIS_PASSWORD=$REDIS_PASSWORD --image docker.io/bitnami/redis:6.2.7-debian-11-r11 --command -- sleep infinity
Use the following command to attach to the pod:
kubectl exec --tty -i redis-client \
--namespace redis -- bash
2. Connect using the Redis® CLI:
REDISCLI_AUTH="$REDIS_PASSWORD" redis-cli -h redis-master
REDISCLI_AUTH="$REDIS_PASSWORD" redis-cli -h redis-replicas
To connect to your database from outside the cluster execute the following commands:
kubectl port-forward --namespace redis svc/redis-master 6379:6379 &
REDISCLI_AUTH="$REDIS_PASSWORD" redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379
安装 Weaviate
helm install weaviate ./weaviate --namespace weaviate[root@localhost charts]# helm install weaviate ./weaviate --namespace weaviate
NAME: weaviate
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Aug 1 11:23:55 2025
NAMESPACE: weaviate
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
安装dify
1、首先配置values.yml文件,注意各配置项需要完善
2、helm upgrade -i dify -f values.yaml dify/dify###################################
# Please replace "dify123456" with your own value
###################################
global:
appSecretKey: 'dify123456'
consoleApiDomain: "console.dify.local"
consoleWebDomain: "console.dify.local"
serviceApiDomain: "api.dify.local"
appApiDomain: "app.dify.local"
appWebDomain: "app.dify.local"
filesDomain: "upload.dify.local"
enterpriseDomain: "enterprise.dify.local"
ingress:
enabled: true
className: "nginx"
annotations: {
# set file upload size limit
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: "15m"
}
api:
replicas: 3
serverWorkerAmount: 1
innerApi:
apiKey: "dify123456"
worker:
replicas: 3
celeryWorkerAmount: 1
web:
replicas: 1
sandbox:
replicas: 1
apiKey: "dify123456"
enterpriseAudit:
replicas: 1
enterprise:
replicas: 1
appSecretKey: "dify123456"
adminAPIsSecretKeySalt: "dify123456"
innerApi:
apiKey: "dify123456"
enterpriseFrontend:
replicas: 1
ssrfProxy:
enabled: true
replicas: 1
unstructured:
enabled: true
replicas: 1
plugin_daemon:
replicas: 1
apiKey: "dify123456"
plugin_controller:
replicas: 1
plugin_connector:
replicas: 1
apiKey: "dify123456"
gateway:
replicas: 1
###################################
# Persistence Configuration
###################################
persistence:
type: "s3"
s3:
endpoint: "http://minio.minio.svc.cluster.local:9000" # Minio 集群内地址
accessKey: "DVasjzqvtTu1VRb1EyC3"
secretKey: "TWDiuCrS5Mq2nh0tHxHkHdd2cs9b5rcns26hPaSZ"
region: "us-east-1"
bucketName: "dify-storage"
addressType: ""
useAwsManagedIam: false
useAwsS3: false # 改为 false 因为使用 MinIO 而非 AWS S3、其他方式按规则修改
###################################
# External postgres
###################################
externalPostgres:
enabled: true
address: "postgresql.postgresql.svc.cluster.local" # 集群内地址
port: 5432
credentials:
dify:
database: "dify"
username: "postgres"
password: "1HKfBeYAVK"
sslmode: "disable"
plugin_daemon:
database: "dify_plugin_daemon"
username: "postgres"
password: "1HKfBeYAVK"
sslmode: "disable"
enterprise:
database: "enterprise"
username: "postgres"
password: "1HKfBeYAVK"
sslmode: "disable"
audit:
database: "audit"
username: "postgres"
password: "1HKfBeYAVK"
sslmode: "disable"
###################################
# External Redis
###################################
externalRedis:
enabled: true
host: "redis-master.redis.svc.cluster.local" # 集群内地址
port: 6379
username: ""
password: "idHjwOXhJ8"
useSSL: false
###################################
# External Qdrant
###################################
vectorDB:
useExternal: true
externalType: "qdrant"
externalQdrant:
endpoint: "http://qdrant.qdrant.svc.cluster.local:6333/" # 集群内地址
apiKey: "test-dify-apikey-qdrant"
imagePullSecrets: []
安装Nginx Ingress Controller
Nginx Ingress 控制器 - Dify Enterprise Docs
wget https://assets-docs.dify.ai/2025/07/727045c765d5052ef3cc2f4b15aaa492.yaml
kubectl apply -f ./727045c765d5052ef3cc2f4b15aaa492.yaml
kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx
vi /etc/hosts
4.152.1.216 console.dify.local
4.152.1.216 app.dify.local
4.152.1.216 api.dify.local
4.152.1.216 upload.dify.local
4.152.1.216 enterprise.dify.local
sed -i s/4.152.1.216/x.x.x.x/g /etc/hosts访问页面输入License激活
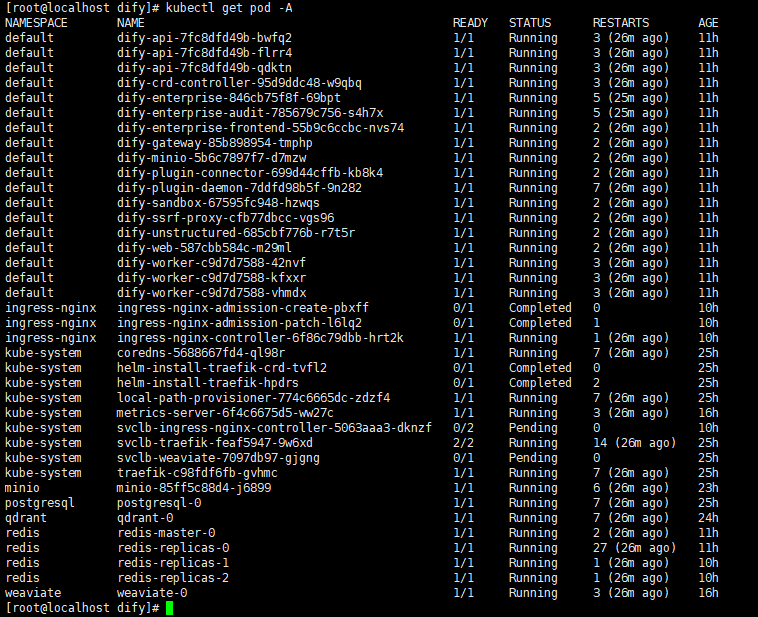
错误原因
dify-api和dify-worker 与s3配置有关


dify-enterprise 和 dify-plugin 与postpresql有关



 提供CDN加速/云存储服务
提供CDN加速/云存储服务